%matplotlib inline
Convert to grayscale
This example shows how to use squidpy.im.process to convert an image
layer to grayscale.
You can convert any layer of squidpy.im.ImageContainer() to grayscale.
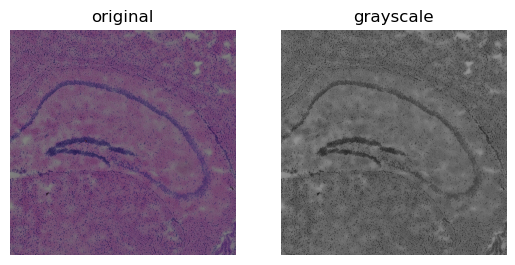
We use the argument method = 'gray' to convert the image. This calls
skimage.color.rgb2gray in the background.
See also
examples_image_compute_smoothexamples_image_compute_process_hires
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import squidpy as sq
First, we load the H&E stained tissue image. Here, we only load a
cropped dataset to speed things up. In general, squidpy.im.process can
also process very large images (see
examples_image_compute_process_hires).
img = sq.datasets.visium_hne_image_crop()
Then, we convert the image to grayscale and plot the result. With the
argument layer we can select the image layer that should be processed.
When converting to grayscale, the channel dimensions change from 3 to 1.
By default, the name of the resulting channel dimension will be
'{{original_channel_name}}_gray'. Use the argument channel_dim to
set a new channel name explicitly. By default, the resulting image is
saved in the layer image_gray. This behavior can be changed with the
arguments copy and layer_added.
sq.im.process(img, layer="image", method="gray")
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2)
img.show("image", ax=axes[0])
_ = axes[0].set_title("original")
img.show("image_gray", cmap="gray", ax=axes[1])
_ = axes[1].set_title("grayscale")